Control Structures are just a way to specify flow of control in programs. They are used for non-sequential and repetitive execution of instructions.
Permalinkif statement
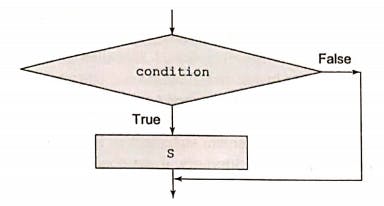
In Python, if statement evaluates the condition as a boolean expression. If the condition evaluates to True, the block of code following the if statement is executed. However, if the condition evaluates to False, the code is ignored and the control is transferred out of the if statement block.
PermalinkSYNTAX
if condition :
statements s
PermalinkFLOW DIAGRAM
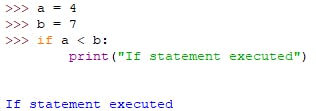
PermalinkEXAMPLE
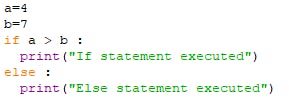
Permalinkif - else statement
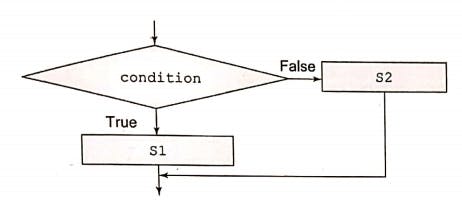
The else statement is to specify the execution of a block of code if the condition in the if statement is false.
PermalinkSYNTAX
if condition:
statements s1
else:
statements s2
PermalinkFLOW DIAGRAM
PermalinkEXAMPLE

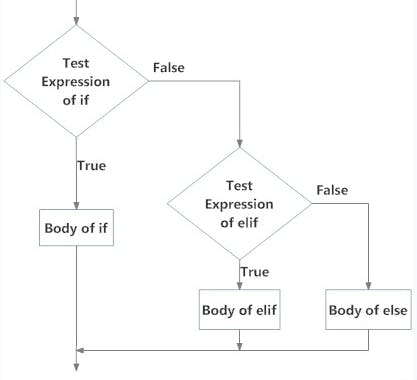
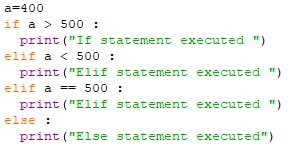
Permalinkif - elif - else statement
The elif is short for else if and is useful to avoid excessive indentation. It is used to check and evaluate multiple expressions for True. There can be n number of elif statements or conditions.
PermalinkSYNTAX
if condition:
statements
elif condition:
statements
else:
statements
PermalinkFLOW DIAGRAM
PermalinkEXAMPLE
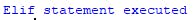
PermalinkWhat are loops?
The process of repetitive execution of a statement or a sequence of statements is called a loop. Execution of a sequence of statements in a loop is known as an iteration of a loop.
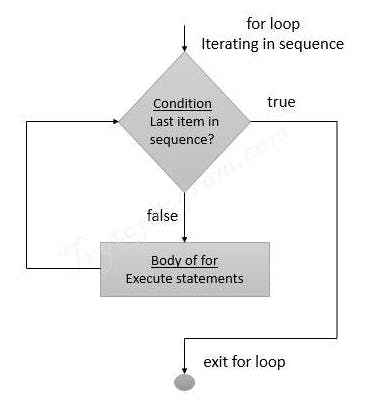
Permalinkfor loop
This loop is used to execute a sequence of statements or instructions for a fixed number of times.
PermalinkSYNTAX
for value in sequence:
statements
PermalinkFLOW DIAGRAM
PermalinkEXAMPLE
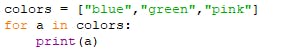
 To loop through a set of code a specified number of times, we can use the
To loop through a set of code a specified number of times, we can use the range() function.


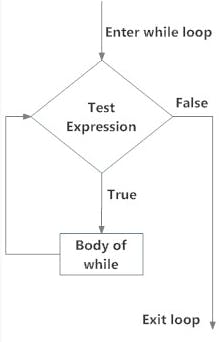
Permalinkwhile loop
This loop is used for executing a sequence of statements again and again on the basis of some test condition. The body of the loop gets executed as long as the test condition holds True.
PermalinkSYNTAX
while <test condition>:
statements
PermalinkFLOW DIAGRAM
PermalinkEXAMPLE


A while loop with a condition that always evaluates to true is called an infinite loop.
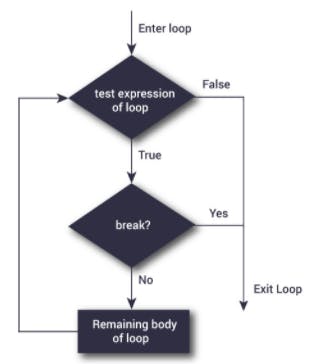
Permalinkbreak statement
This statement can alter the flow of a normal loop. It enables us to exit the loop and transfer the control to next iteration of the loop. If the break statement is inside a nested loop (loop inside another loop), the break statement will terminate the innermost loop.
PermalinkSYNTAX
break
PermalinkFLOW DIAGRAM
PermalinkEXAMPLE


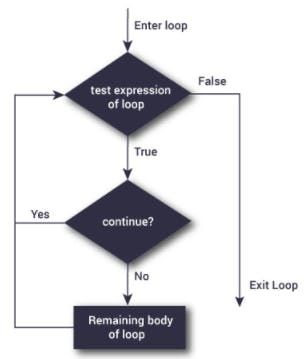
Permalinkcontinue statement
This statement is used to transfer the control to next iteration of the loop. When it gets executed, the code that occurs in the body of the loop after the continue statement is skipped.
PermalinkSYNTAX
continue
PermalinkFLOW DIAGRAM
PermalinkEXAMPLE


Permalinkpass statement
This statement is a null statement and executes no code. However, it is different from comments. The difference is that while the interpreter ignores a comment entirely, pass is not ignored.
PermalinkSYNTAX
pass
PermalinkEXAMPLE


With this we come to an end of control structures. Stay tuned for more easy learning notes and keep practicing !!