Logical operators are those operators which are used to combine two or more expressions and yield the results as either True or False.
not operator
This is a unary logical operator which requires only one operand.
True => False
False=> True
and operator
This is a binary logical operator which involves two operands.
True True => True
True False => False
False True => False
False False => False
or operator
This is a binary logical operator which involves two operands.
True True => True
True False => True
False True => True
False False => False
The above is also their order of precedence decreases from top to bottom i.e. not operator has highest precedence and the or operator has the lowest!
Short-circuit evaluation of boolean expression
While evaluating an expression that involves an and operator, the second sub-expression is evaluated only if the first sub-expression yields as True. If the first sub-expression yields False, then python does not evaluate the second sub-expression; thus determining the value of whole expression as False. This is called as short-circuit evaluation of boolean expression.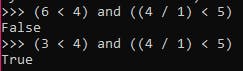
Similarly, While evaluating an expression that involves an or operator, the second sub-expression is evaluated only if the first sub-expression yields as False.
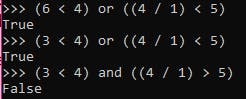
Now, the precedence of arithmetic, logical and relational operators in decreasing order is as follow.
Arithmetic Operator
Relational Operator
Logical Operator
Hope you are following the notes.Stay tuned for more!
